To genuinely understand customers and increase retention, businesses need to focus a big part of their resources and manpower on customer feedback. The way someone approaches feedback can make or break their business.
In this guide, we’ll show you just how valuable customer feedback can be and give some actionable tips on how to collect and act on it.
How Important Is Customer Feedback?
Feedback represents your customers’ positive experiences, frustrations, and pain points. It reveals why some clients love your brand and what’s preventing others from doing so. Basically, customer feedback allows looking into a customer’s perception of your brand and encourages targeted actions meant to increase customer satisfaction.
Considering all that, it’s safe to say that focusing on customer feedback and making business decisions based on it can bring in several advantages, including the following:
Help You Improve Your Product and Services
Customer feedback tells you exactly what changes to make to ensure existing customers continue doing business with you. For instance, feedback on customer services can let you know if your support team requires additional training, more manpower, or other resources to meet customer demands.
Product feedback can alert you to issues ruining the customer experience or feature requests that can boost it.
Marketing feedback can let you know if your copy is too aggressive, vague, or incorrect (like marketing text accidentally claiming your service can be integrated with a specific 3rd party service when it actually can’t).
Boost Referrals
Satisfied customers are more likely to tell others about your business – it’s as simple as that. Statistics show that happy customers tell up to nine people on average about their positive experiences with a company.
Moreover, according to data, 90% of consumers check online reviews before doing business with a company. What’s more, around 88% of them trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations.
Improve Customer Loyalty
The happier customers are with your brand, the more likely they are to stick around. According to research, about 74% of B2B buyers are willing to spend more money to continue doing business with a company that offers great service. What a customer defines as excellent customer service can range from great and prompt support to UI tweaks that streamline the customer experience.
Drive More Profit
Considering the above, this is pretty obvious. With loyal customers, retention is skyrocketing, referrals are driving more leads and your company is streamingly growing.
Besides that, research shows that highly-engaged customers will make purchases 90% more frequently and spend 60% more money per transaction.
What Is the Customer Feedback Loop?
In short, it’s a customer relationship management strategy that involves the collection and implementation of customer feedback. It’s often called the ACAF loop due to its four stages:
- Asking customers for feedback.
- Categorizing the received feedback.
- Acting on the feedback (sharing it with relevant departments, fixing bugs, etc.).
- Following up with customers to let them know about the improvements.
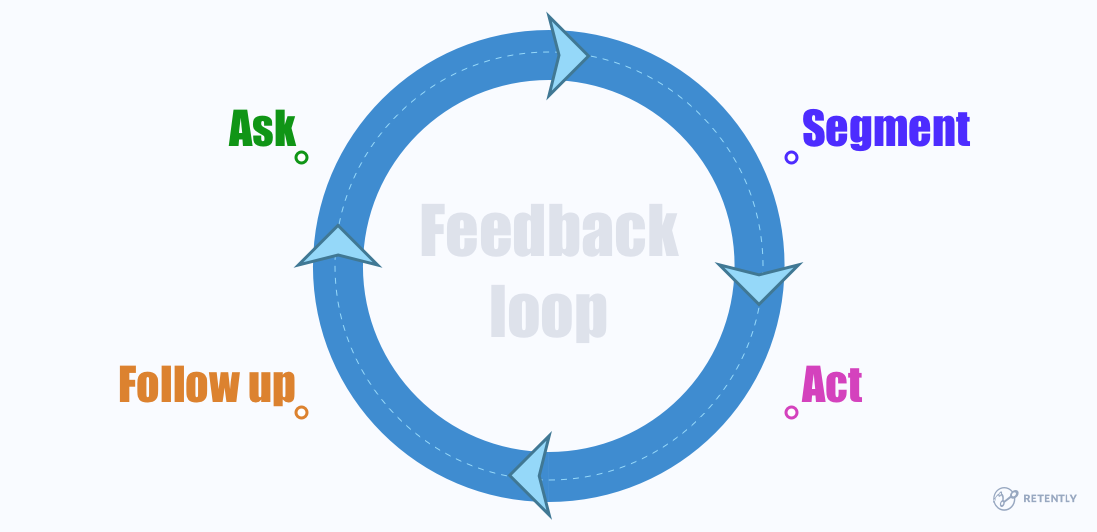
So, overall, the customer feedback loop is a continuous cycle in which you gather feedback, analyze, act, and follow up on it.
Acting on the feedback by implementing solutions ASAP, acknowledging how important customers’ suggestions were, and responding to clients to let them know reported issues were fixed are great ways to close the feedback loop. Doing that significantly boosts the customer experience since it shows how committed the business is to understanding their pain points and helping them achieve the desired results.
Plus, there’s a chance that not doing the above could potentially cause some clients to think their feedback isn’t taken seriously. So, a closed-loop system can put their concerns to rest, likely boosting satisfaction and loyalty rates.
How to Get Actionable Customer Feedback
Here are the six most efficient customer feedback methods – the ones that allow you to gather actionable data.

Before we start, though, here’s one thing you should keep in mind – customer feedback has to be collected and segmented for every step of the customer journey. You can’t get useful insights if you don’t do that.
Now, let’s dive into the most actionable methods and learn how to get the most out of them.
1. Monitor Social Media
When customers want to complain about a problem, mention bugs or glitches, or praise a brand, they don’t always reach out directly to the company. Instead, they’ll often post about it on social media, expecting your business to address their feedback. Right now, it seems that around 54% of people prefer to do that. And solving their complaints that way won’t just improve your image. It will also save you money since it’s six times less expensive to solve a customer issue on social media than through a call center, for instance.
Of course, keeping track of social media mentions on all relevant platforms isn’t really possible. Even if you have a whole team handling it, it would still take too much time and effort – resources that could be better spent on a different area of your business. Sure, some people might send you direct messages on social media, making things a bit easier, but not all customers will do that. Some of them will just talk about you in comments or posts where they won’t tag or link to your business.
Luckily, you can use social media monitoring tools that alert you whenever your brand is mentioned on various social media websites. Mention, Brand24, and Youscan are pretty decent options that help you quickly identify online mentions of your brand. Having your team use those tools to monitor social media feedback will be much more efficient. Just make sure they focus on the following things when analyzing social media comments and posts:
- The customer’s sentiment (positive, neutral, or negative).
- The main issues and themes recurring across most comments.
- The voice tone that was used (satisfied, frustrated, sarcastic, angry, etc.).
That way, relevant feedback can be collected and acted on in due time.
2. Create Feature Request Boards
As the name implies, a feature request board is an online board where customer requests are posted, stored, and analyzed by the product development team. You can either ask customers directly what new features and improvements they’d like to see or give them access to the board so they can post their suggestions or vote on existing ones.
There are plenty of reasons to use feature request boards:
- It makes your customers feel like their voices are actually heard and that they’re actively contributing to your product roadmap.
- It eliminates much of the guesswork involved in product development since you know exactly what your high-intent clients want the most.
- Your customers might feel a stronger bond with your brand, which could improve their loyalty.
- You’ll have an easy-to-use channel through which you can make users feel more appreciated by letting them know when you will implement their suggestions.
As for how you can do this, there are plenty of options. If you have the time and manpower, you can create a private Facebook group where customers can post their suggestions. Though, something like that only works well if you have many active and engaged customers. If you don’t, getting them to interact can be a bit difficult.
An easier way to collect data for the product roadmap is using a product like Canny – a user-friendly platform for collecting and organizing feature requests.
Alternatively, you can use other services to create feature request boards and gather customer feedback:
3. Use Customer Feedback Surveys
A customer survey is a great way to collect relevant data (referral potential, satisfaction rates, trust levels, etc.) from your audience. Customer feedback forms can be used too, but they are not as versatile as surveys. Plus, they tend to be longer, so clients may not be as inclined to spend their time filling them out.
Collecting feedback with surveys is pretty simple since they can be sent through emails, as in-app surveys, or through messaging platforms like Intercom. As for what types of surveys you can use, here are your options:
NPS (Net Promoter Score)
NPS is a type of survey that lets you track growth indicators which show how loyal your customers are, how likely they are to refer your brand to others, and how happy they are with your products and services. NPS customer feedback survey questions usually go something like this:
“How likely are you to recommend our business to a friend or work colleague?”
NPS surveys feature just one question, but they also use follow-up questions (one follow-up question is the general rule). Also, NPS scores can vary between -100 and 100, and responses are measured on a scale from 0 to 10. Respondents are segmented into the following categories:
- Detractors (0-6)
- Passives (7-8)
- Promoters (9-10)
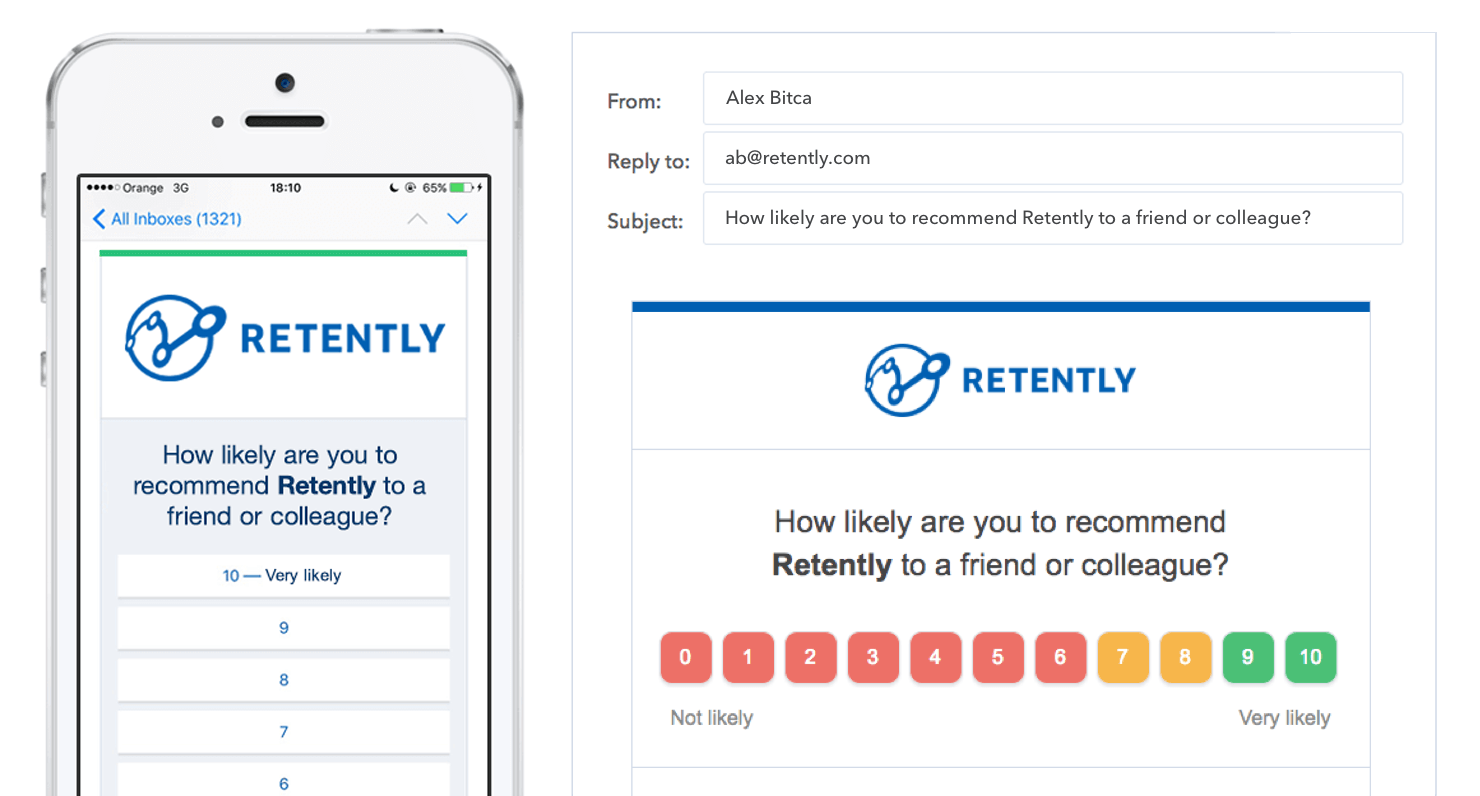
If you’d like to learn more about NPS, check out this article.
CSAT (Customer Satisfaction Score)
As the name implies, CSAT customer feedback surveys measure how satisfied your clients are with your business. They track how customers reacted to an action your business took, or how they feel after interacting with your website, services/products, or marketing materials. CSAT surveys use the following type of customer feedback questions:
“How would you rate your overall satisfaction with the service you received?”
The responses are pretty flexible. They can be in the 1-10 or 1-5 range, or they can range from “Very Dissatisfied” to “Very Satisfied.” CSAT surveys can contain just one question or multiple ones, and CSAT scores vary from 0% to 100%.
In case you’d be interested to learn how CSAT compares to NPS and CES, here’s a guide we wrote on that topic.
CES (Customer Effort Score)
CES surveys measure how easy or difficult it is for customers to interact with your brand, services, and products in order to find out how happy or unhappy they are with your business. CES surveys normally use just one customer feedback question, which can be worded differently depending on the rating scale:
- Statement – “The company made it easy for me to solve my problem.”
- Question – “How easy was it for you to solve your problem?”
- Rating – “Please rate how easy it was for you to solve your problem.”
As for how CES handles scoring, there are multiple options:
- Likert scales – The answers can be numbered from 1 to 7, and are in the “Strongly Disagree – Strongly Agree” scale: Strongly Disagree – Disagree – Somewhat Disagree – Undecided – Somewhat Agree – Agree – Strongly Agree.
- Emoji faces – The answers include a Happy Face, a Neutral Face, and an Unhappy Face.
- 1-10 ratings – Usually, the 1-3 responses will be a positive indicator, while the 4-10 responses will indicate that customers are finding it difficult to interact with your brand.
- 1-5 ratings – Answers only include “Very Difficult – Difficult – Neutral – Easy – Very Easy,” and can be numbered from 1 to 5.
Due to the varied types of responses, calculating the CES score usually just comes down to analyzing the responses and calculating an average.
Want to learn more about CES surveys? Here’s everything you need to know.
5-Star
5-star surveys are one of the most straightforward types of customer feedback surveys. They are used to measure how satisfied customers are with your business by asking them a question like:
“How would you rate your experience with our company/specific transaction?”
Respondents can offer a 1-star, 2-star, 3-star, 4-star, or 5-star rating. 4 and 5-star ratings are normally considered positive responses, while 1 and 2-star ratings are considered bad signs. As for the 3-star rating, it can be seen as being a neutral response, but it can also mean the customer is not fully satisfied with your brand. The score is usually calculated by doing an average. For more insights on 5-star surveys, check this article.
4. Customer Meetings
Customer meetings are a great way to have a conversation with clients about what improvements they’ve seen and what features or changes they might like in the future. Ways to get useful feedback include:
- Asking customers what they found easy and/or difficult about achieving success with a specific service/product.
- Focusing on what features, offers, and marketing messages made customers find the products/services most appealing.
- Finding out in what areas the products/services exceeded customer expectations and what areas need improvement.
Customer meetings don’t always have to take place face-to-face. Phone interviews are still an efficient, low-effort, and budget-friendly way to contact clients and ask them for their input.
Also, trade shows and conferences are suitable environments to interact with customers and ask for feedback. Having a dedicated team engage with existing clients at the booth or throughout the event will help a lot.
Besides that, customer panels are also a great source of feedback, but only as long as they include key decision-makers from companies that are current clients. Decision-makers outside the client base can also be hired to offer insights from a potential customer’s perspective.
5. Quarterly Business Reviews (QBR)
QBRs (Quarterly Business Reviews) are pretty similar to customer meetings, but they take place regularly, usually every three months. Also, they are generally reserved for very loyal and profitable clients, and executives from both sides (your company and the customer’s company) present to discuss how well your products and services have helped your client perform. Your product/service’s ROI will be highlighted even more since you will have plenty of long-term benchmarking data to back it up during QBRs.
All in all, customer meetings are an excellent way to gather feedback that helps you quickly solve issues and make your brand more attractive for existing and potential clients, while QBRs reveal what improvements or changes are needed for existing customers to remain loyal, and continue doing business with you in the long run.
6. Live Chat
Live chat is becoming increasingly important. Around 79% of customers prefer using live chat to any other medium because it’s convenient and fast. Those stats are hardly surprising. Live chat lets your sales and customer service teams solve and answer customer issues very quickly. What’s more, if you also use chatbots, potential and existing clients can get the solutions they need in seconds.
Also, recurring issues can be highlighted by your customer service team and forwarded to the product development or marketing team. Plus, the feedback that’s collected through live chat is very valuable since users who use live chat are worth 4.5 times more than those who don’t.
You can have the live chat feature present all over your website or just on specific pages, like the help or pricing page. Having the live chat option available on the pricing and payment pages could encourage potential customers to get in touch and solve issues that are preventing them from going ahead with the purchase.
7. Implement Comment Boxes
Comment boxes are text fields usually located at the bottom of a web page. Their purpose is to ask website visitors or product users if they have any suggestions or complaints about the page they’re on. With that data, you can improve your copy, content, and UX to the point where it’s easier to convert leads into customers and address concerns.
Why use comment boxes and not pop-up messages, though? After all, pop-up messages are more noticeable.
Well, they are, but they’re also more intrusive and – for some people – interrupting and annoying. They can easily break the flow of a user’s actions, including making purchases or checking out your product features.
A comment box at the bottom of the page doesn’t distract website visitors as much as one at the top (on the left or right side of the page) or pops up randomly after a few seconds. But make sure they are just empty fields where users can type in their feedback. Don’t use customer feedback forms since they can feel like extra work to your customers. Just keep it as easy to understand and use as possible.
As for how to use comment boxes, well, you obviously collect customer feedback with them, but you can do much more:
- Thank them for their input, and encourage even more relevant feedback.
- Offer early access to new features and updates to customers asking about them.
- Connect customers who complain about bugs or glitches directly to your tech support team.
- If users are asking about a feature you don’t have yet, offer them directions on how to achieve the desired results with a feature that already exists (if possible).
How to Manage Customer Feedback
Alright, now that you have so many ways to collect actionable customer feedback, what do you do with it? Well, before you start acting on it, you need to make sure you have an efficient customer feedback system in place where you can store all collected data. Otherwise, you won’t be able to do much with all that feedback since you’ll quickly lose track of the main themes and issues.
Many businesses make the mistake of simply relying on Google Sheets documents. While it’s a useful management system when you have only a few customers, it’s unreliable as your business grows. While you can use different Excel or Google Sheets tabs for each type of feedback, all that data will soon become overwhelming and hard to manage.
Instead, you should sync and store all your customer feedback in a CRM. For example, if you use survey software, you can sync and export all the results to your Salesforce or HubSpot account. That way, all your departments will have a simple way to access and analyze feedback data, identify customer journey trends, and close the feedback loop.
Besides that, consider implementing relevant tags on the messaging platforms you use to collect feedback. That makes it easy to filter customer communications and find specific discussions where certain issues or suggestions were mentioned.
And, if you really want to save tons of time and effort, you should try using customer feedback software that lets you store all the data you get from surveys, customer feedback questionnaires, QBRs, social media posts, and messages in a central hub.
How to Best Use Customer Feedback
The main thing you need to do with customer feedback is identify improvement areas for your product, service, and customer support, then prioritize them accordingly. Feeding the feedback into your product roadmap will also boost your customer acquisition efforts.
But that’s not enough. You need to make sure that all departments in your company have access to appropriate feedback data. You can not expect your customer support teams to improve their services if they don’t have access to relevant customer service data.
That’s why you need to take the time to segment the feedback and share it with the appropriate departments. Notifying the heads of each department through instant messaging alerts is a good start, but you should invest in content creation, too – like showcasing the main feedback takeaways in newsletters, videos, slideshares, or infographics. That way, you ensure all the data is easier to understand for everyone.
Feedback sharing doesn’t stop at your employees. Such data should also be discussed with people in executive positions and stakeholders during your meetings. Of course, not every type of feedback has to be highlighted – just the most recurring issues that might need additional funding and manpower or any other resources you wouldn’t be able to get without stakeholder’s approval.
Once everyone properly understands your customers’ needs and issues, it’s time to take action on all that feedback. See which changes should be tackled first (usually, issues like bugs, not understanding how the service/product works, or other complaints), and assign them to the right teams.
Lastly, once a problem has been fixed or a suggestion implemented, follow up with the respective customers to notify them. Some easy ways to do that include:
- Sending personalized thank-you emails to your customers.
- Mailing thank-you letters to those who offered extremely valuable feedback.
- Rewarding clients who provided very actionable data.
- Publishing reports that show how you implemented solutions based on the received inputs.
Conclusion
Customer feedback is the bread and butter of any successful business. It tells you what issues your clients are dealing with and what loyal customers love about your product or service. Acting on it makes it possible to boost profits, drive referrals, and increase customer loyalty. Just make sure you use the right customer feedback tools to gather and manage data, conduct customer feedback analysis, and follow up with users once improvements have been made.
If you know any other ways of collecting actionable customer feedback, let us know – we’d love hear your input.
















 Greg Raileanu
Greg Raileanu 

 Alex Bitca
Alex Bitca 


 Christina Sol
Christina Sol